We continue this series to demystify some tech “buzzwords.” This time, we’ll explore what a Headless CMS (HCMS) is.
We’ll start by understanding why this concept emerged through a brief history of the web and CMSs, then explain exactly what an HCMS is, its advantages, and how you can leverage it.
TL;DR
A Headless CMS is a content management system focused exclusively on creating, storing, and delivering content, without handling how that content is presented to the end user.
This allows developers to use any frontend technology—or even any type of application—to display it, delivering flexibility, performance, and scalability.
A Bit of History
With all the solutions available today… why do we need something new?
Let’s briefly review how we got here to understand why an HCMS makes so much sense.
The Beginning: a Static Website
Company websites often contain a lot of information that rarely changes—like “About us,” “What we do,” or “Contact us.” In that scenario, the most direct approach is to build a static website with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
The problem arises when you want to update something: you must edit the code and upload it to the server. In other words, even changing a paragraph requires technical skills.
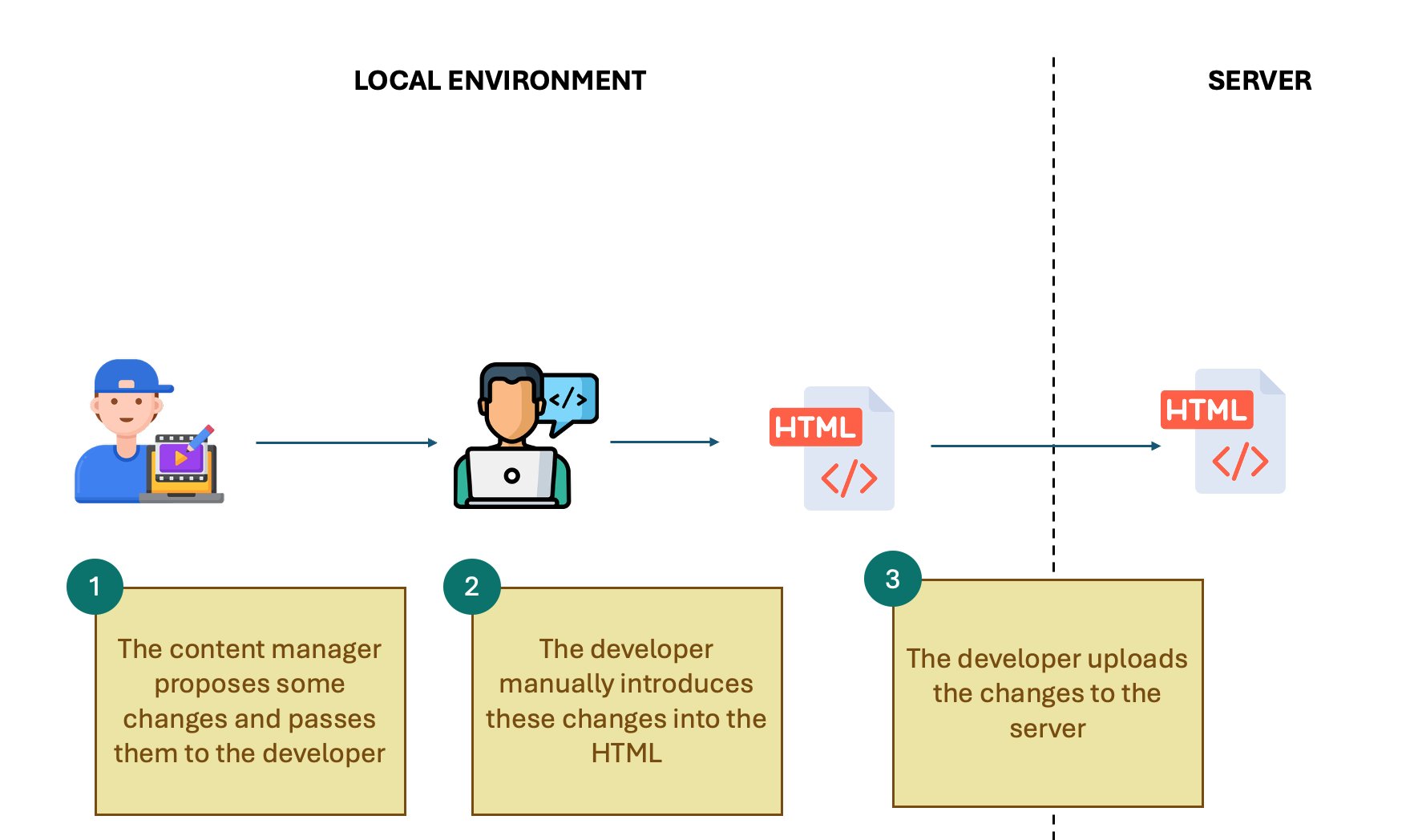
Advantages of a static website:
- Very easy to implement
- Fast and secure
- Easy to deploy
- Minimal attack surface
Clear disadvantages:
- Requires both content editor and developer
- Not scalable for frequently updated content
- No code reuse, high maintenance
The Homemade Solution: Your Own “Admin”
The next step is creating a custom admin panel, separating the public site and the content editor backend.
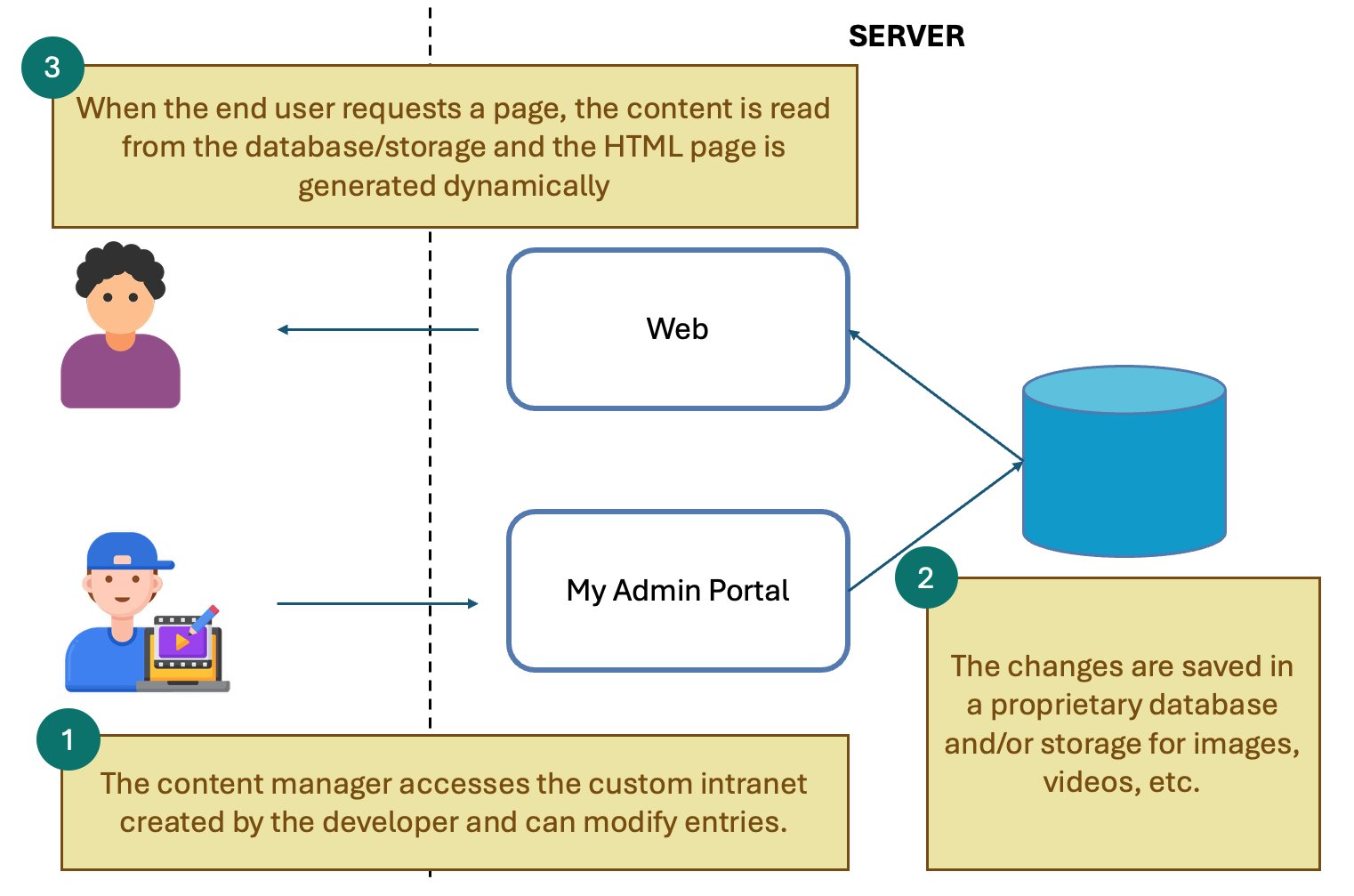
Advantages:
- Full control
- Editors don't need to code
Disadvantages:
- Extra work: frontend + admin
- Security, UX, infrastructure — all on you
- Dynamic pages can be resource-heavy
The Rise of Traditional CMSs (WordPress, Joomla…)
All-in-one solutions like WordPress let you build a site without coding.
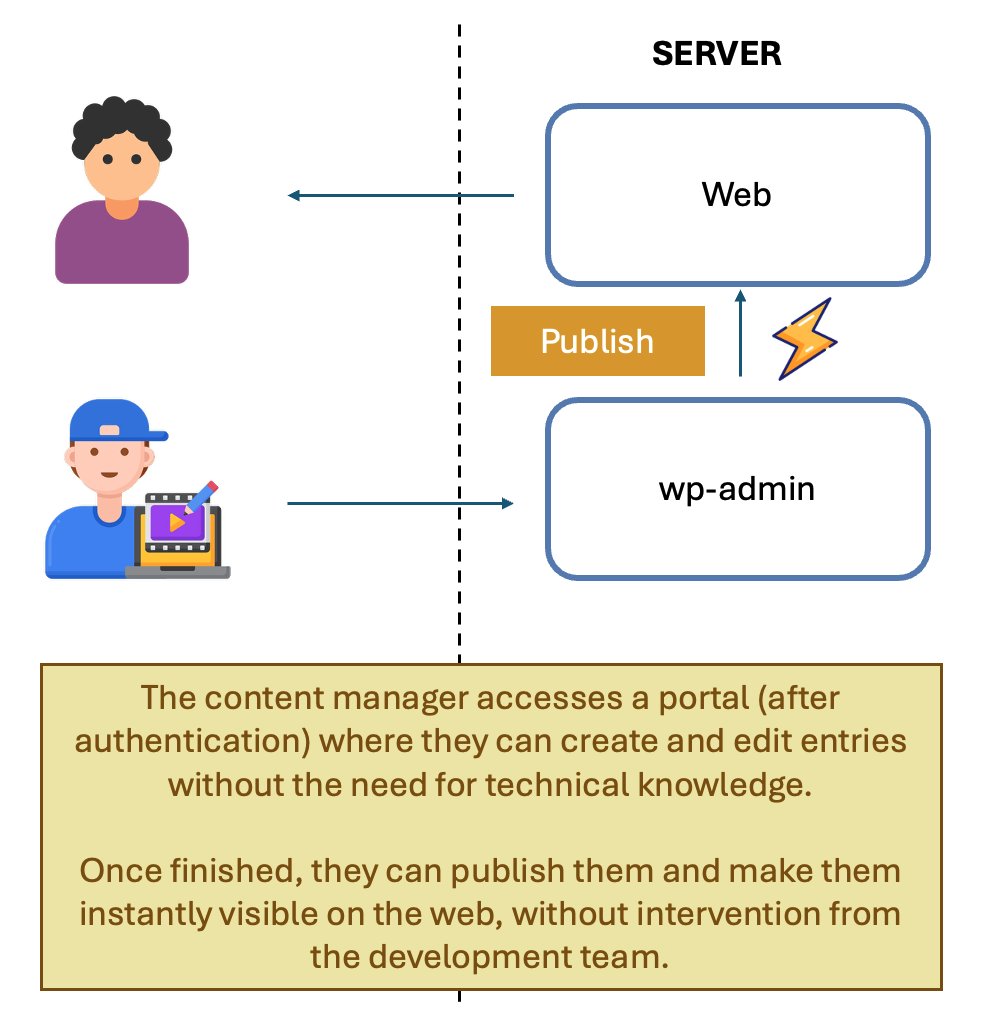
WordPress options:
- Use a theme
- Build your own
Hosting options:
- WordPress.com (PaaS)
- Self-hosted
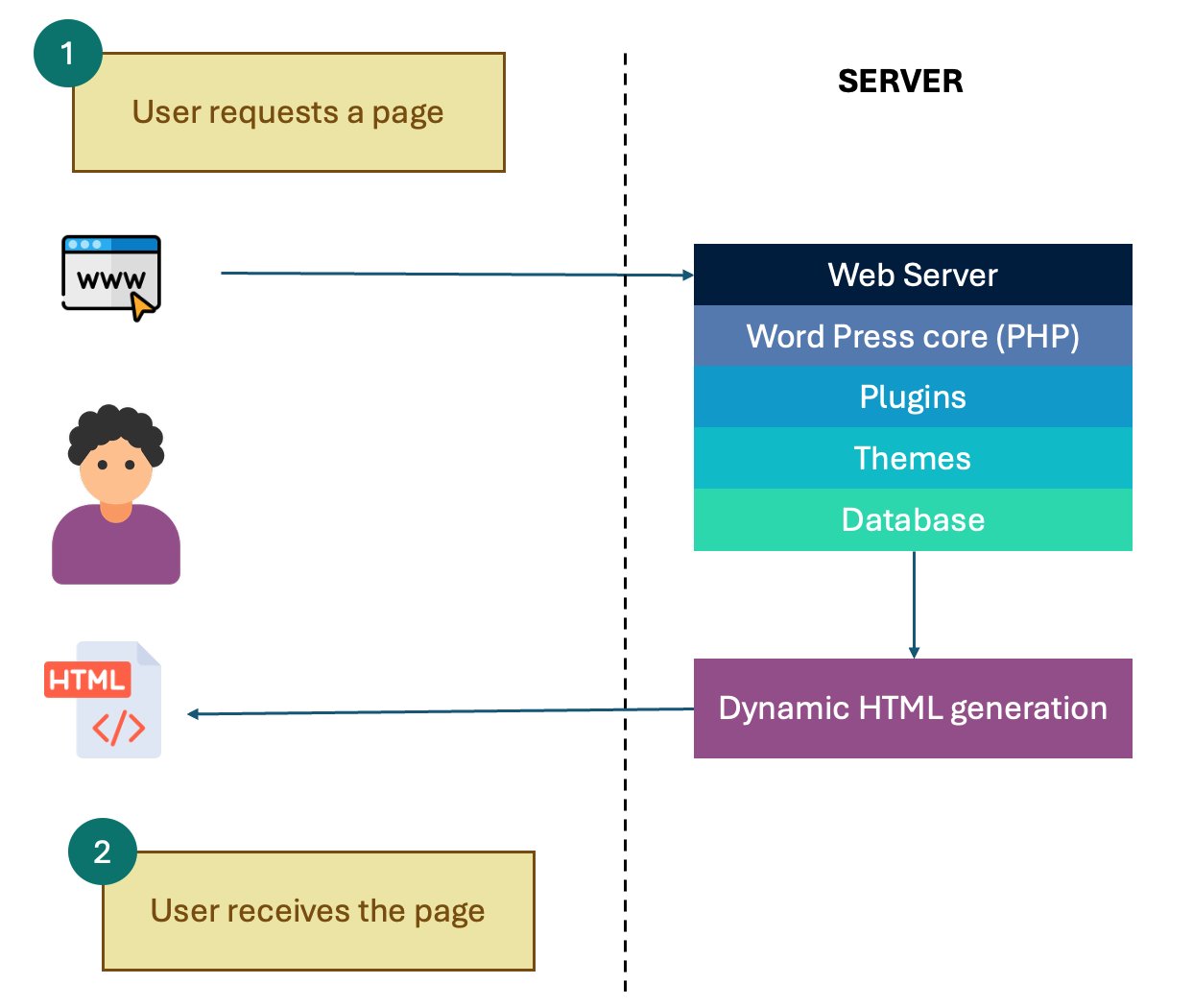
Each page request triggers:
- Theme load
- PHP execution
- DB query
- HTML rendering
Advantages:
- Fast if needs fit
- Plugins & themes galore
- Large community
Disadvantages:
- Tech lock-in
- Updates needed for security
- Plugins can be buggy
- Not ideal for custom needs
Separating Content from Presentation
Developers fetch data via APIs and control the UI.
Headless CMS does this for editorial content.
It structures and exposes content via APIs for use anywhere.
No frontend enforced.
Why “Headless”?
No built-in frontend: just create and serve content.
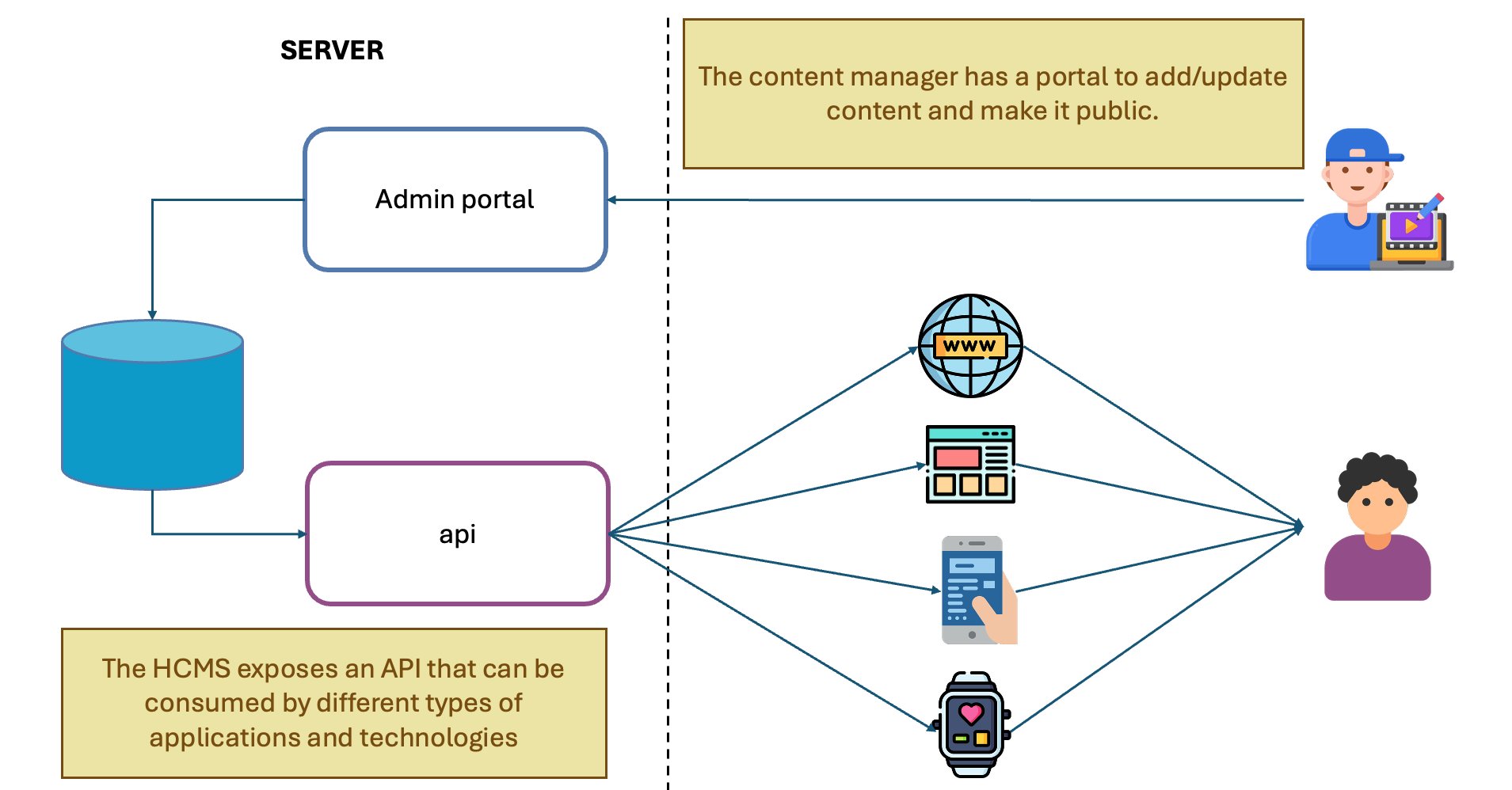
Typical Workflow of a Headless CMS
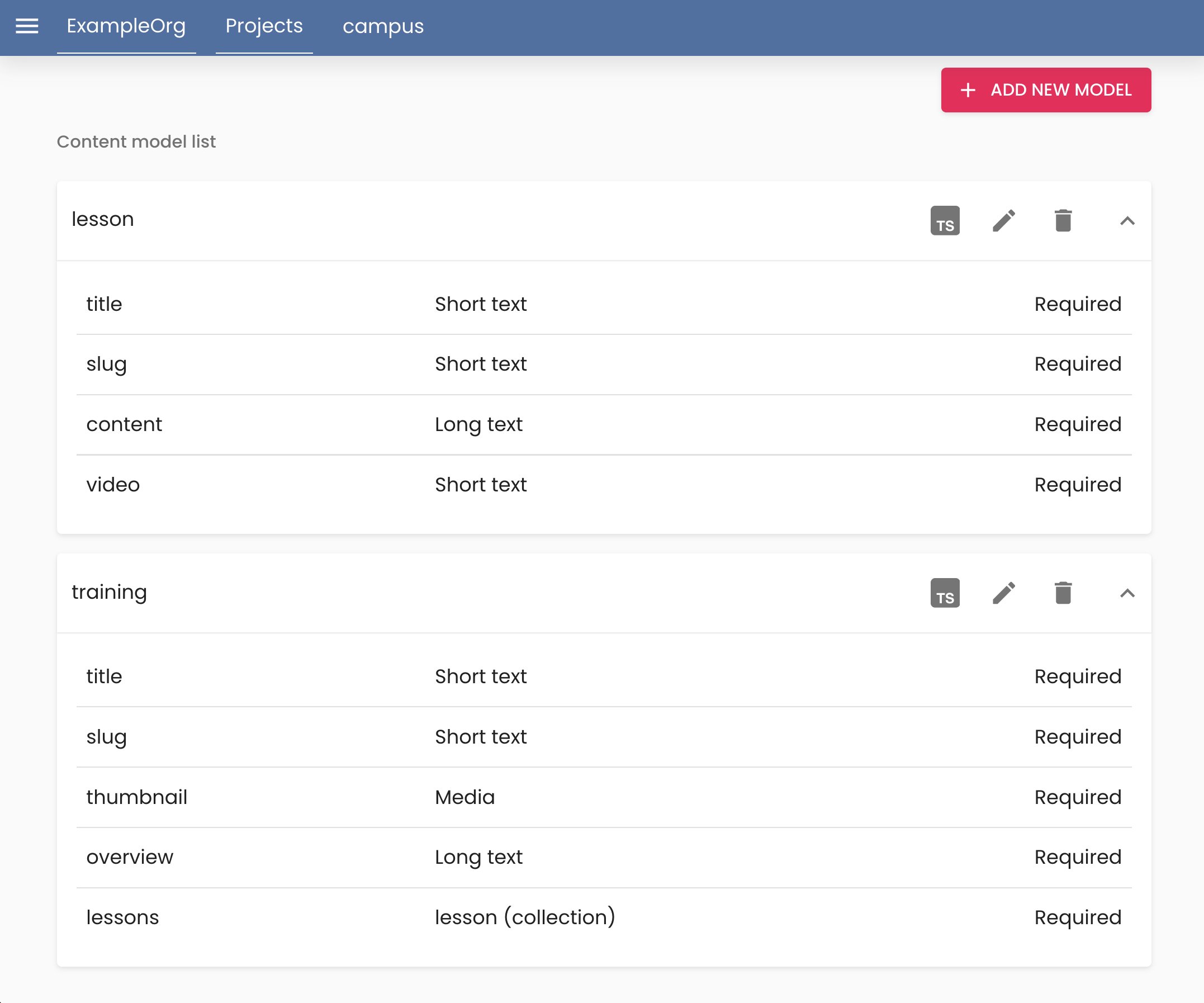
Content Creation
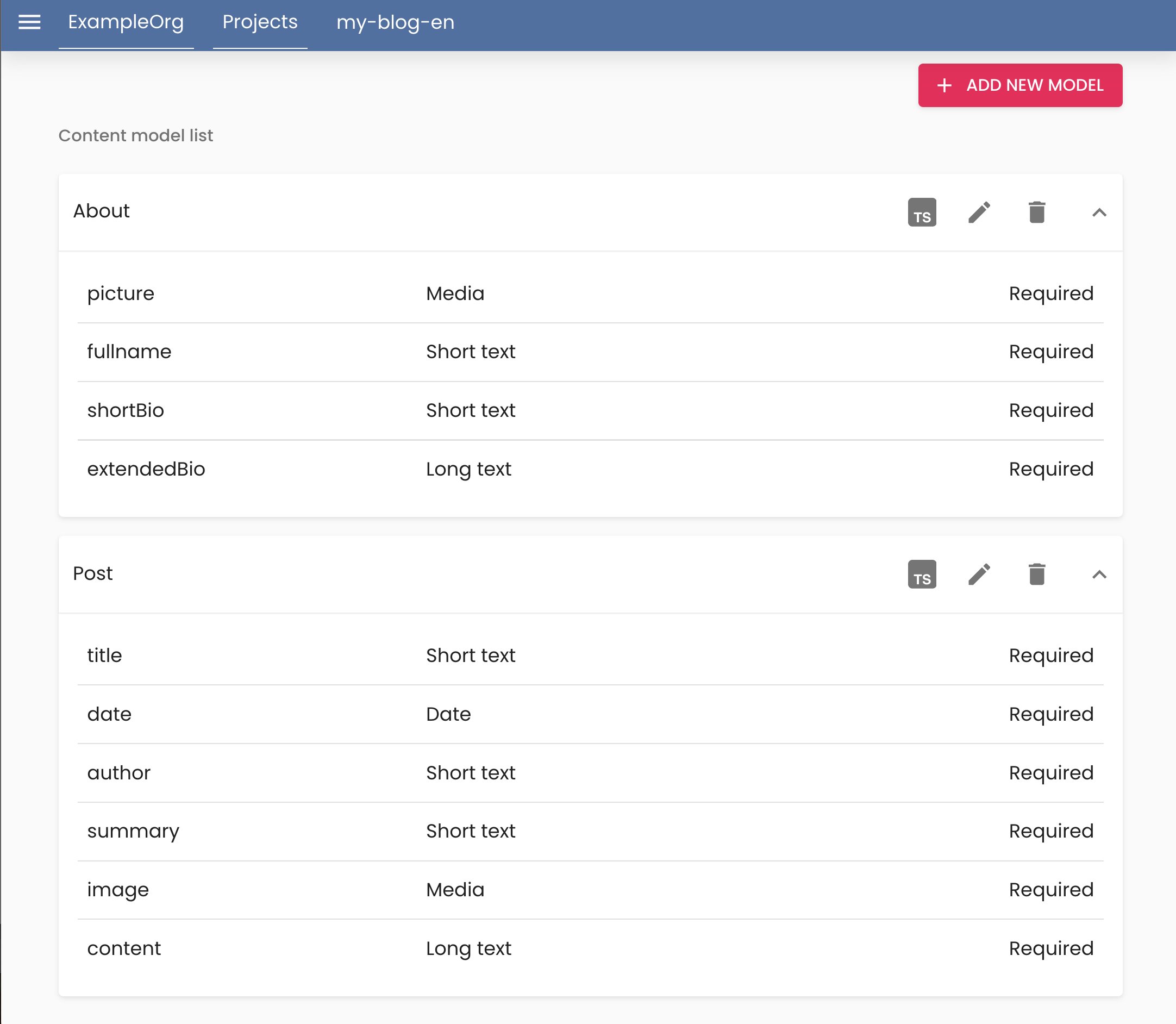
Model entities:
- “About” → name, photo, bio
- “Post” → title, content, date, author
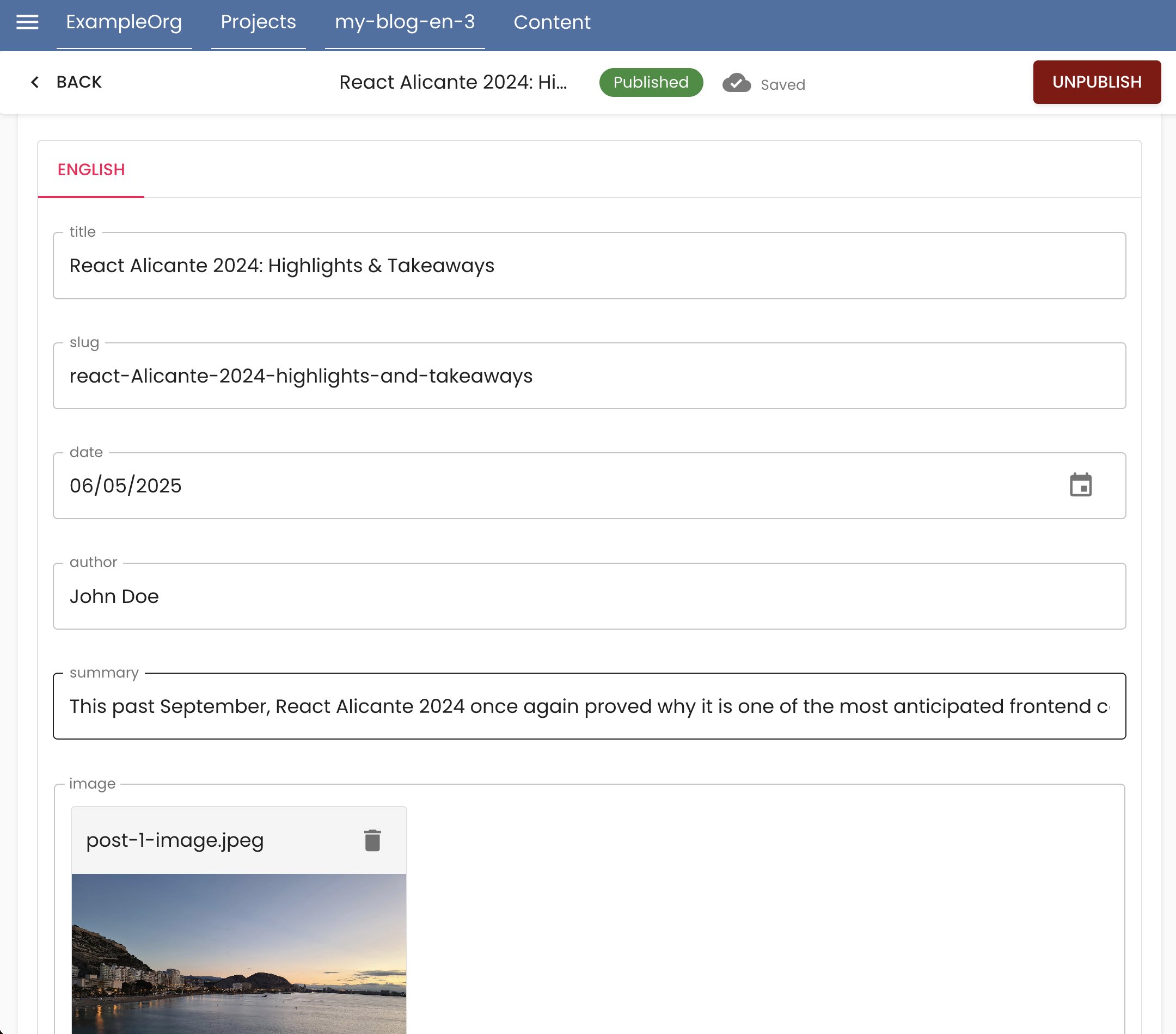
Content is entered visually, served via REST or GraphQL.
Assets served via CDN.
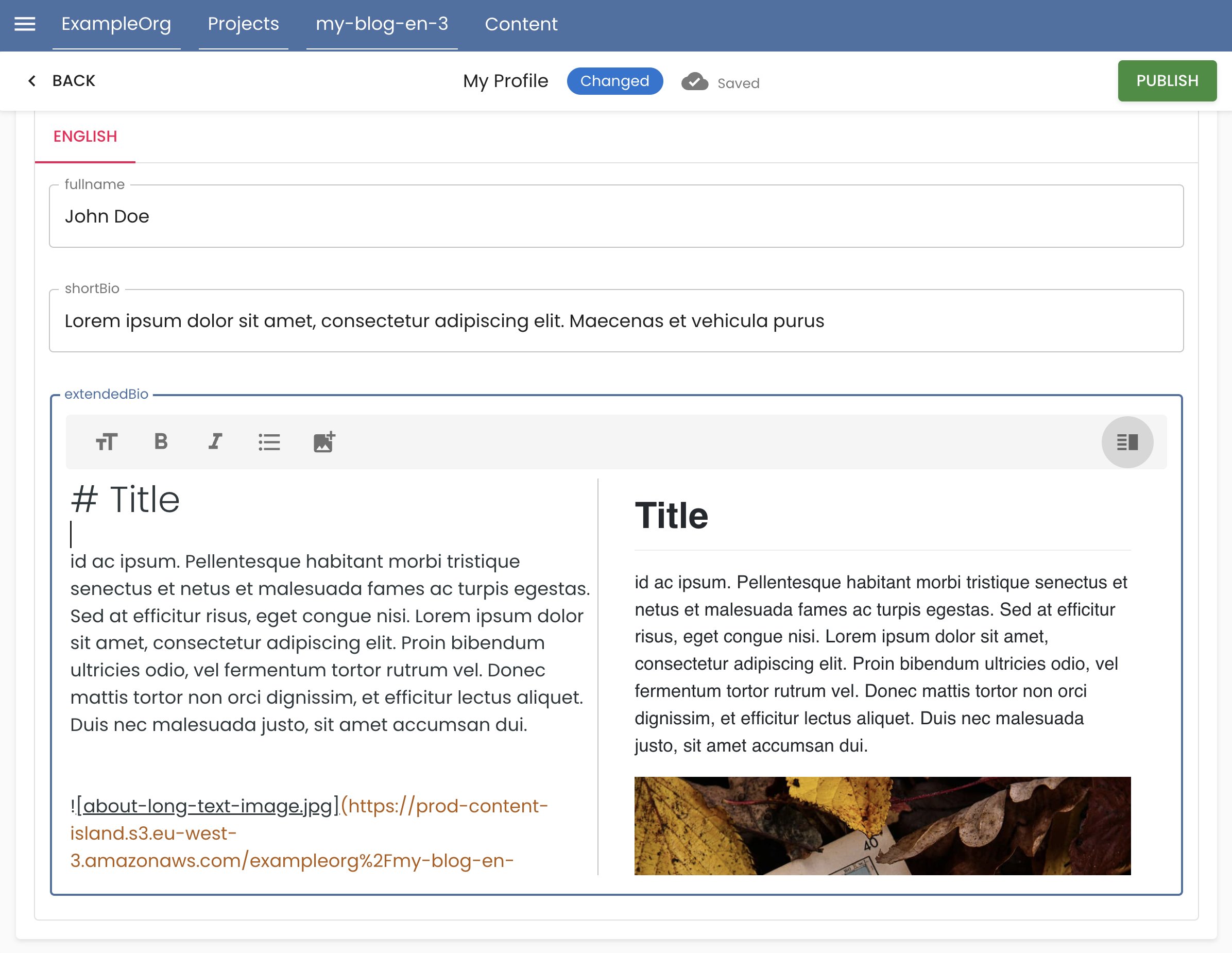
Supports Markdown for rich content:
Supports entity relationships:
Content Consumption
Consume via REST or GraphQL with any frontend framework.
import { CONTENT_ISLAND_SECRET_TOKEN } from "astro:env/server";
import { createClient } from "@content-island/api-client";
export const client = createClient({
accessToken: CONTENT_ISLAND_SECRET_TOKEN,
});import client from "../../lib/client";
import type { SinglePost } from "./post.model";
export async function getPosts(): Promise<SinglePost[]> {
const posts = await client.getContentList<SinglePost>({
contentType: "Post",
});
return posts;
}Supports filtering, sorting, pagination.
Pair with a custom backend as needed.
Advantages of Headless Model
✅ Use any frontend
✅ Better performance & security
✅ Highly scalable
✅ Team separation
✅ Reusable content
Disadvantages
⚠️ Requires frontend development
So… Is WordPress Dead?
No. It still works depending on:
- Project type
- Team
- Budget
- Scalability needs
Examples of Headless CMSs
- Content Island – Modern HCMS with free plan and paid from €12/month
- Contentful – Enterprise-friendly, starts at $300/month
- Strapi – Self-hosted or PaaS, paid per project from $15/month
Conclusion
Headless CMS separates the what (content) from the how (presentation), giving teams more flexibility and control.
In a multi-platform world, a central content source that can serve any frontend is a major win.
Try It Yourself
Create a free account on Content Island